What is OWASP Dependency Track
OWASP Dependency Track is a great open source tool to manage all 3rd Party Dependencies in your products. Your CI/CD Pipeline can continuously send software bill of material files (SBOM) after each build to the Dependency Track Application’s backend API.
Dependecy Track downloads (mirrors) locally a copy of the National Vulnerability Database and continuously checks if one of your components has a known issues. As soon as a new vulnerability is publicly reported, your team can get a notification by email or by instant message on platforms like Slack or Mattermost.
Deploy OWASP Dependency Track with PostgreSQL database using Docker Compose
OWASP Dependency Track documentation already has instructions how to deploy the environment using Docker Compose: https://docs.dependencytrack.org/getting-started/deploy-docker/. For trying out this tool locally it’s sufficient.
But for production, H2 database in the OWASP Dependency Track installation needs to be replaced with PostgreSQL or MySQL. Following instructions will help you to configure it with persistancy.
Docker-compose with persistency
Below you can find a sample Docker Compose yml file with extra services added for storing your component and vulnerabilities permanently in a PostgreSQL database. It also has Adminer Database Management tool in the compose file for managing the data if needed.
Make sure that you have Docker Engine installed locally before trying to run the Docker Compose command as described here: Install Docker Engine | Docker Documentation
Download the docker-compose.txt with PostgreSQL
Click here to download as a .txt file. Change the extention to .yml after downloading it locally and run it using “docker compose up ” command.
Blank element
docker-compose.yml contents - click to expand
version: ‘3.7’
#####################################################
# This Docker Compose file contains two services
# Dependency-Track API Server
# Dependency-Track FrontEnd
# Postgres Database
# Adminer Database Management UI
#####################################################
volumes:
dependency-track:
db:
driver: local
services:
postgresdb:
image: postgres
restart: always
environment:
– POSTGRES_USER=dtrack
– POSTGRES_PASSWORD=dtrack #TODO: change this!
ports:
– ‘5432:5432’
volumes:
– db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
adminer:
image: adminer
depends_on:
– postgresdb
restart: always
ports:
– 8082:8080
dtrack-apiserver:
image: dependencytrack/apiserver
depends_on:
– postgresdb
environment:
# The Dependency-Track container can be configured using any of the
# available configuration properties defined in:
# https://docs.dependencytrack.org/getting-started/configuration/
# All properties are upper case with periods replaced by underscores.
# Required properties:
– ALPINE_WORKER_THREADS=0
– ALPINE_WORKER_THREAD_MULTIPLIER=4
– ALPINE_DATA_DIRECTORY=~/.dependency-track
– ALPINE_WATCHDOG_LOGGIN_INTERVAL=0
# Database Properties
– ALPINE_DATABASE_MODE=external
– ALPINE_DATABASE_URL=jdbc:postgresql://postgresdb:5432/dtrack
– ALPINE_DATABASE_DRIVER=org.postgresql.Driver
– ALPINE_DATABASE_USERNAME=dtrack
– ALPINE_DATABASE_PASSWORD=dtrack
deploy:
resources:
limits:
memory: 12288m
reservations:
memory: 8192m
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
ports:
– ‘8081:8080’
volumes:
– ‘dependency-track:/data’
restart: unless-stopped
dtrack-frontend:
image: dependencytrack/frontend
depends_on:
– dtrack-apiserver
environment:
# The base URL of the API server.
# NOTE:
# * This URL must be reachable by the browsers of your users.
# * The frontend container itself does NOT communicate with the API server directly, it just serves static files.
# * When deploying to dedicated servers, please use the external IP or domain of the API server.
– API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8081 #TODO: change your URL!
ports:
– “8080:8080”
restart: unless-stopped
Production environment warning
Make sure to change default passwords for PostgreSQL in your copy of the Docker Compose file. Set the password at least by using Environment variables or use Docker Secrets.
Using OWASP Dependency Track
After starting the docker compose, navigate to the http://localhost:8080/ URL
Use default credentials as documented here: https://docs.dependencytrack.org/getting-started/initial-startup/
- username: admin
- password: admin
You will be asked for a new username and password upon first login.

Create a new project
Projects in the OWASP Dependency Track represent a software product, library, framework, service that can consist of many other components. You can create one project per your SBOM file that is generated during the build process in your CI/CD pipeline.


Upload SBOM file
You can find specification about the CycloneDX SBOM files here: https://cyclonedx.org/
There are many tools available for generating the SBOM files, check here the full list: https://cyclonedx.org/tool-center/
Ideally your build pipeline should automatically upload new SBOM files after each nightly build using OWASP Dependency Track automation API (see next chapter). But it is also possible to upload your file via the Components tab of your Project.

Integrate OWASP Dependency Track in your CI/CD Pipeline
Official OWASP Dependency Track documentation has a page explaining how you can push a new SBOM from your build pipeline: https://docs.dependencytrack.org/usage/cicd/
Examples of API usage:
curl -X "POST" "http://dtrack.example.com/api/v1/bom" \ -H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data' \ -H 'X-Api-Key: LPojpCDSsEd4V9Zi6qCWr4KsiF3Konze' \ -F "project=f90934f5-cb88-47ce-81cb-db06fc67d4b4" \ -F "bom=<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>..."
Project Identifier
Project argument above is the Object identifier from the “View Details” link on your Project.


It is also possible to auto create a project if it doesn’t exist with API by using the autoCreate argument.
curl -X "POST" "http://dtrack.example.com/api/v1/bom" \ -H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data' \ -H "X-Api-Key: xxxxxxx" \ -F "autoCreate=true" \ -F "projectName=xxxx" \ -F "projectVersion=xxxx" \ -F "bom=@target/bom.xml"
X-Api-Key
You can find the X-Api-Key token for automation under the Automation team details. You can also create a new team with a different token and define access rights for the API.
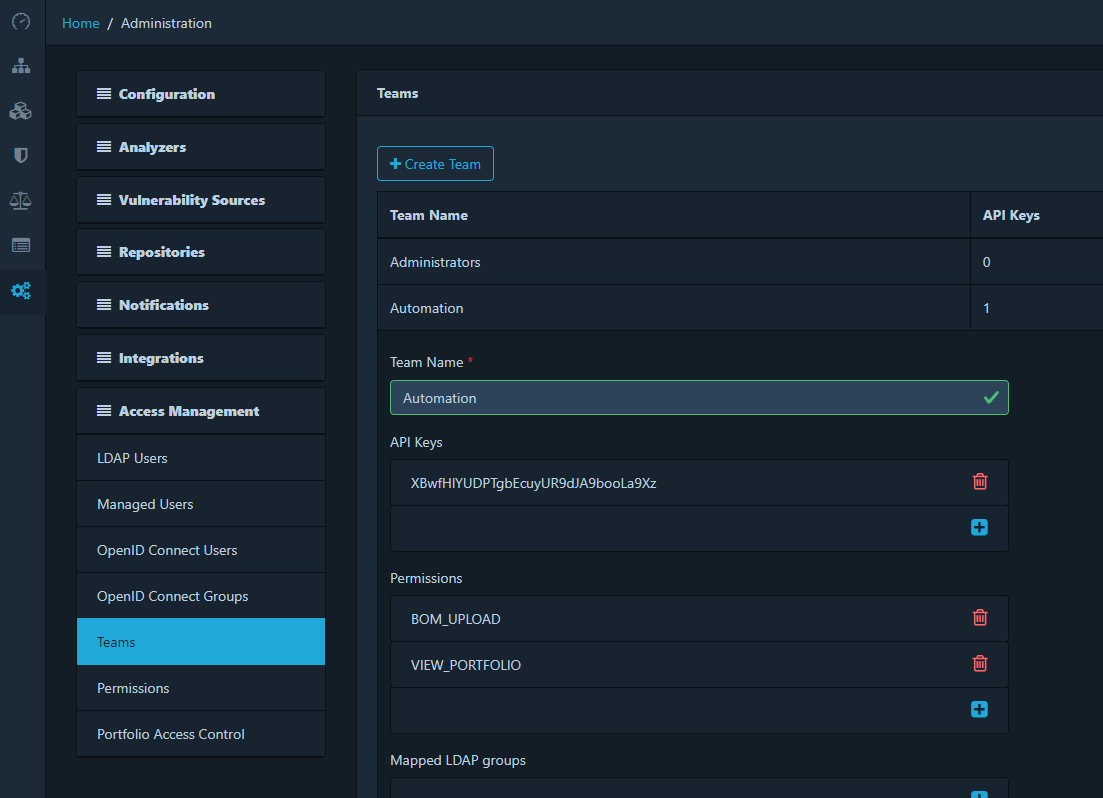
Using Adminer Database Management Tool
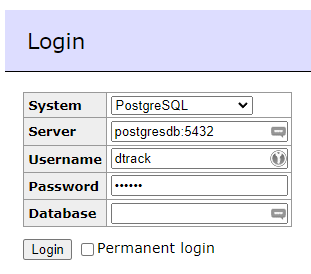
Although not necessary for the production deployment, it can be handy to have an option to connect to your PostgreSQL database instance in your container. Docker-compose file above already has Adminer service in it. Feel free to remove it for your production environment.
After launching the container, navigate to http://localhost:8082 and enter following information:



0 Comments